We must have the courage to strike out in new directions and embrace an economic model which is not only low-carbon and environmentally sustainable, but also turns poverty, inequality and lack of financial access into new market opportunities for smart, progressive, profit-oriented companies.
Reference: Business and Sustainable Development Commission (2017, p7)
The framework for contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through the Integrated Report <IR> value creation process set out in this blog. This involves below five step process:
- Include all sustainable development issues relevant to the organization’s external environment;
- Mature integrated thinking, connectivity and governance;
- Recognise material sustainable development issues that affect value creation;
- Develop the goals and strategy to contribute to the SDGs through the business model;
- Develop and communicate the integrated report
Sustainable development requires a systemic response involving transformative changes, notably
in knowledge, policy and institutional systems from all sections of society. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the Paris Agreement1, SBTi2, EP1003 are few example of global multi-stakeholder responses to this challenge. The SDGs are inter-dependent and contributing to them involves trade-offs, just as an organization’s outcomes involve trade-offs between multiple capitals (see the <IR> Framework4).
An integrated report demonstrate how an organization creates value over the time. Value is not created by or within an organization alone. It is:
- Influenced by the external environment
- Created through relationships with stakeholders
- Dependent on various resources and Capitals
Reference: International <IR> Framework, IIRC
The International <IR> Framework (IIRC, 2021) can be used to assistance understanding of the relationship between sustainable development and value creation further trade-offs across the interdependent and potentially conflicting SDGs. It does this by:
- taking into account of risks and opportunities presented by the external environment;
- adopting a multi-capital approach;
- recognising that creating value over time requires social and environmental stewardship and creating value for investors and other relevant stakeholders;
- enabling high-level engagement and a holistic approach (integrated thinking) through its emphasis on connectivity and board oversight.
Supporting business approaches to the SDGs with Integrated Reporting can redirect investment flows to maximize value creation. Further it enhance the knowledge of impact of business activities on sustainable development. Such type of culture and strategy help to assist organizations in reducing risk, identifying opportunities and delivering long-term, innovative solutions and technologies for addressing sustainable development.
Source:https://unfoundation.org/




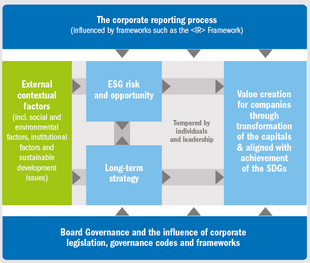
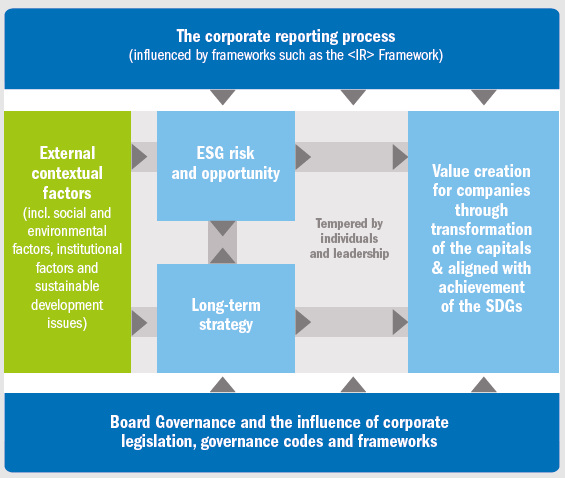


A framework for contributing to the SDGs through the <IR> value creation process
Source: Adapted from Adams (2017)
[1] https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement
[1] https://sciencebasedtargets.org/
[1] https://www.theclimategroup.org/ep100
[1] https://integratedreporting.org/resource/international-ir-framework/
Conceptualization of the corporate value creation process: below 5 steps can be applied to align the SDGs to the value creation process
Step 1:
Recognise sustainable development issues relevant to the organization’s external environment:
The sustainable development issues that the SDGs address impact on the organization’s ability to create value for itself and its stakeholders. The <IR> Framework requires consideration of significant factors that affects the external environment and the organization’s response. These influencing factors may increase or decrease the value created either directly (e.g., by creating new business opportunities) or indirectly (e.g., through the quality of relationships with stakeholders or by influencing the availability, quality and affordability of a capital that the organization uses or affects). Therefore, consideration of the SDGs, and the sustainable development issues that they address, should be incorporated into the wider consideration of the external environment relevant to the organization’s ability to create value.
Step 2:
Identify material sustainable development issues that influence value creation:
The materiality process for Integrated Reporting involves identifying, evaluating and prioritizing matters supported their ability to affect value creation within the short, medium and future. Value is made for the organization and for others through increases, decreases and transformation of the capitals. Therefore, when planning their approach to the SDGs, organizations seeking to reassess their mission and purpose and/ or to scale back corporate risk and increase opportunities arising from sustainable development issues should identify, evaluate and prioritize which sustainable development issues maximize outcomes for the six capitals and hence their contribution to the SDG targets19.
Step 3:
Develop strategy to contribute to the SDGs through the business model:
The organization’s strategy identifies how it intends to mitigate or manage risks and maximize opportunities. Organizations should began their strategic objectives and methods to support relevant and significant SDGs through their business model. This could incorporate resource allocation plans and specific, quantified short, medium and long-term targets.
Step 4:
Develop integrated thinking, connectivity and governance:
The Framework calls on organizations to link their strategy to changes within the external environment including evolving societal expectations and natural resources limitations. Further, it emphasizes the importance of responding to the legitimate needs and interests of stakeholders because value is made through its relationships with others. It recognizes that these interests are often in conflict and should require trade-offs. Those charged with governance are required to acknowledge their involvement and responsibility for this process. Those charged with an organization’s governance should satisfy themselves that:
- the processes of building relationships with stakeholders will: identify material sustainable development issues; that these are incorporated into strategy; and, that appropriate goals and targets are developed.
- the organization develops and nurtures relationships with and between stakeholders so as to reinforce collective well-being;
- the organization’s business model considers all material sustainable development issues impacting on inputs and outcomes in terms of the six capitals;
- the organization’s strategy and business model evolve to reflect past performance with reference to the SDGs.
Step 5:
Prepare the integrated report:
Organizations should report on key sustainable development issues which impact on stakeholders and therefore the organization to influence value creation within the short, medium and future. Organizations should report their contribution to SDG targets alongside their outcomes with reference to the six capitals.
SDGs only having been agreed at the end of 20155. Reporting of SDG as part of <IR> Report is now developing. We can expect to see increasing innovation in integrating thinking for the SDGs linking them with strategy and incorporating them into <IR> reports. We at TUV India, performs the third party assurance of <IR> report and supports the organization to disclose verified key material topic and all six capitals2. TUV India provides indepedent assurance of public/ committed disclosures on sustainability performance as well as underlying systems, data & processes against the suitable criteria and standards like <IR>, GRI, AA1000AS,ISAE 3000 (revised).
About The Author
TUV India Pvt. Ltd.
TÜV NORD GROUP
certificationindia@tuv-nord.com